Table of Contents
What is Smart Agriculture? And which roles do IoT, Big Data, and AI play in the industry’s digital transformation? In this article, we highlight the potential of digital technology for solving the urgent challenges in Japan’s agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and food industry.
Key Take-Aways
- Smart agriculture refers to the utilization of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, location systems, robots, and artificial intelligence (AI) on farms.
- The main goal of smart agriculture is to achieve greater food self-sufficiency and revenues by compensating for environmental risks of crop failures and increasing overall yield quality.
- Tailor-made IoT devices and AI solutions are preferable in order to maximize efficiency and output. By training machine learning models with both new and existing information, yield prediction becomes a reality.
What is Smart Agriculture?
Farmers always have to deal with the whims of nature: winds, frosts, heat – environmental influences are a major risk. A loss of harvest poses an enormous economic threat, even more so for small-scale farms. To compensate for losses and optimize crops, farmers traditionally had to rely on intuition, experience, and outdated history data.
Japanese agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and the food industry, heavily depend on the labor of highly skilled workers. However, the age of farmers in Japan is rising while the interest in farming by young adults is declining. At the same time, farmland is scarce and self-sufficiency in food has hit a record low in recent years. Environmental factors are a growing threat.
As a countermeasure, even very traditional industries like agriculture are increasingly utilizing IoT, Big Data, and AI. These technologies are expected to counter the pressures of increasing food demand and climate changes. Utilizing modern technology as part of broader digital transformation initiatives has become a significant requirement of reducing labor and ensuring manpower.
The overall objective of smart agriculture efforts is to achieve greater self-sufficiency and larger revenues by minimizing the risks of crop failures and increasing the overall yield quality.

How To Utilize AI for Yield Prediction and Optimization
One approach to digital transformation in the agriculture industry is the deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT devices are sensor-equipped tools that are connected to the internet. Combined with artificial intelligence, such smart devices can be implemented to increase yields and productivity, while reducing crop failures. They do so by monitoring, analyzing, and forecasting data.
In contrast to off-the-shelf solutions, we recommend tailor-made IoT devices and AI solutions that specifically cater to one’s specific requirements. No matter if it is the implementation of image and infrared sensors, thermal cameras, moisture and humidity sensors, or sound sensors – customization is what makes smart agriculture solutions truly multi-sensory and powerful.
These IoT devices can be used in tractors and trucks, as well as in fields, soil, and plants, to collect data in real-time. Farmers gain insight into light, temperature, and moisture levels. They can analyze topography and soil, or leverage satellite and radar imaging technologies through smart algorithms. The data collected is combined with other available information, such as historic weather and crop data, or aerial imagery. With all of the data gathered, machine learning models are trained to identify patterns – making AI yield prediction a reality.

AI and Automation Are Transforming Agriculture
From small rice and tea farmers to fruit orchards, and even large agricultural holdings – AI (through the use of computer vision and deep learning) allows the automation of processes that previously had to be done manually. Examples are the automation of harvesting and crop sorting, or precision irrigation to save water. Furthermore, IoT devices such as Edge AI cameras can be deployed in the field, while drones generate aerial imagery. AI-based image analysis and machine learning algorithms then count fruit, monitor and predict fruit size, detect pest and plant diseases, and even forecast yield.
To ensure a smooth and automated workflow from collecting and accumulating, to processing and analyzing such Big Data, we strongly recommend deploying a data management tool or AI platform (like our end-to-end solution Avinton Data Platform). The ability to turn data into actual business value is what characterizes a data-driven organization – it is where smart agriculture becomes a reality.
Try our AI object detection demo here. Simply upload an image of an apple tree and let AI image analysis technology detect and count the fruit.
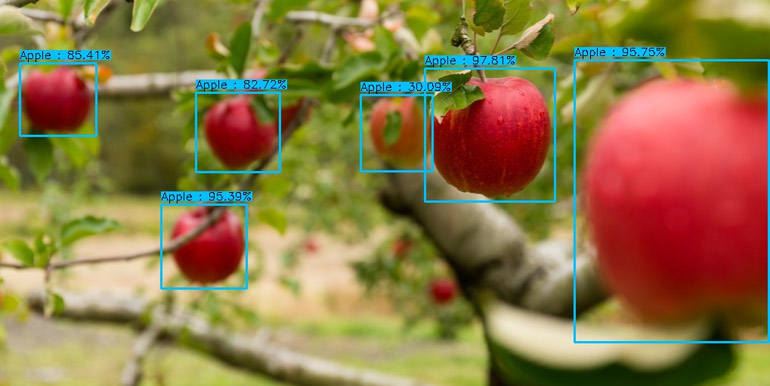
Smart Agriculture and Precision Farming Use Cases
- Yield forecasting and optimization
- Precision irrigation and waste reduction
- Smart sensing and mapping
- Crop health monitoring and fruit counting
- Climate monitoring and forecast
- Livestock tracking and geofencing
- Supply chain optimization (smart logistics and warehousing)
This versatile but incomplete list of use cases shows that digital transformation has already started in the agriculture industry. “Smart agriculture” and “precision farming” have become a reality.
As a Japanese company, we want to contribute our services to the increase of the country’s food self-sufficiency while achieving environmentally sustainable agriculture. We offer strategic support for digital transformation projects and holistic AI consulting. By utilizing our custom-made Big Data and AI solutions, farmers will benefit from saving time and resources, avoiding crop failures as well as increasing yield, food quality, and overall revenue.
We will be happy to provide you with more information.


