In the wake of increasing digital transformation initiatives, most companies these days are well aware of the necessity of data utilization in order to stay competitive and innovative in the future. More than one-third of worldwide digital transformation investment is spent in process and discrete manufacturing.
With the rapidly expanding internet of things (IoT), shop floors in the manufacturing industry will soon include hundreds of billions of connected industrial assets. These IoT devices – ranging from machines to sensors – operate continuously and in real-time. This results in unprecedented amounts of so-called Big Data – data volumes that are too large, too complex, too fast-moving or too weakly structured to be analyzed using manual and conventional data processing methods. Big Data presents manufacturing companies with a major challenge, highlighting the need for new digital technologies.
In Industry 4.0 – or the “factory of the future” – image processing technology is a crucial component that helps drive industrial automation. In this article, we will discuss high-potential use cases for implementing technologies like Edge AI and Machine Vision into manufacturing companies. And as true digital transformation does not end at the stage of implementation, this article will also propose ways to achieve an end-to-end data workflow that generates actual business value. After all, by utilizing the latest tools in data analytics, we want to solve core business problems and help companies stay competitive and innovative.
What is Edge AI?
Be it for the automation of processes or for the analysis of large amounts of data: intelligent and self-learning systems are becoming increasingly important in manufacturing processes. Until now, these intelligent systems have always had to be connected to a cloud, as this provides the large computing power for the mathematical algorithms.
With Edge AI, the next generation of intelligent systems is now on the horizon: the intelligence is shifted from a remote cloud into the end devices themselves. These devices can be attached to various sensors, generating data continuously. Instead of transferring all of this data to the cloud first, Edge AI devices process and analyze it locally and in real-time. The key benefits of Edge AI include the securing of data sovereignty, the improvement of data economy, and the reduction of latency.
What is Machine Vision?
Machine Vision refers to applications that use image capturing and image processing technology to automate industrial production processes. In concrete terms, this means that cameras are installed on manufacturing shop floors, often as part of an Edge device. These cameras continuously capture image data which is instantly processed and analyzed on an attached nano-computer. The results are passed on to downstream systems in the form of actions or specific control signals.
Machine Vision technology allows operators to monitor machinery and the movement of factory workers, and to carry out quality checks and dimensional inspections faster and more accurately than ever before. It requires robust, fast, reliable, and stable systems that can withstand the demands of the industrial environment (such as strong mechanical loads, high or low temperatures, and other adverse environmental conditions).
Functionality and Components of Machine Vision
Machine Vision uses a combination of different hardware devices and software for image capturing and image processing. Central components of Machine Vision are:
- Lighting technology
- Cameras with a specific image sensor technology
- (Nano-)computers for image processing
- Software for image processing and image analysis
- Components connecting to the other production systems
Depending on the application and the task to be performed, the camera technology used varies greatly – ranging from regular images or videos of objects to the creation of 3D images, thermal images, or even X-rays. The large quantity of raw image material created by the cameras is transferred via direct interfaces or network technology to an integrated computer unit or to an external computer for further processing. There, software processes the image material, analyzes it, detects certain features and feeds the analysis results into a decision logic.
Industrial image processing often takes place in real-time, which is why the corresponding transmission capacity and computing power must be available. The results are passed on along the process chain in the form of decisions or direct control commands.
Machine Vision x Deep Learning
For AI-based processing and analysis, Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) come to mind, for example. These technologies can independently categorize objects by analyzing image-based Big Data. To do this, they learn specific patterns that are typical for certain features and thus for classification into a corresponding object class. Such a learning process is similar to training: images of different objects to be recognized are sorted (“labeled”) according to a specific identity or class. The models (“classifiers”) trained in this way can then be used to classify newly acquired images into the previously learned classes.
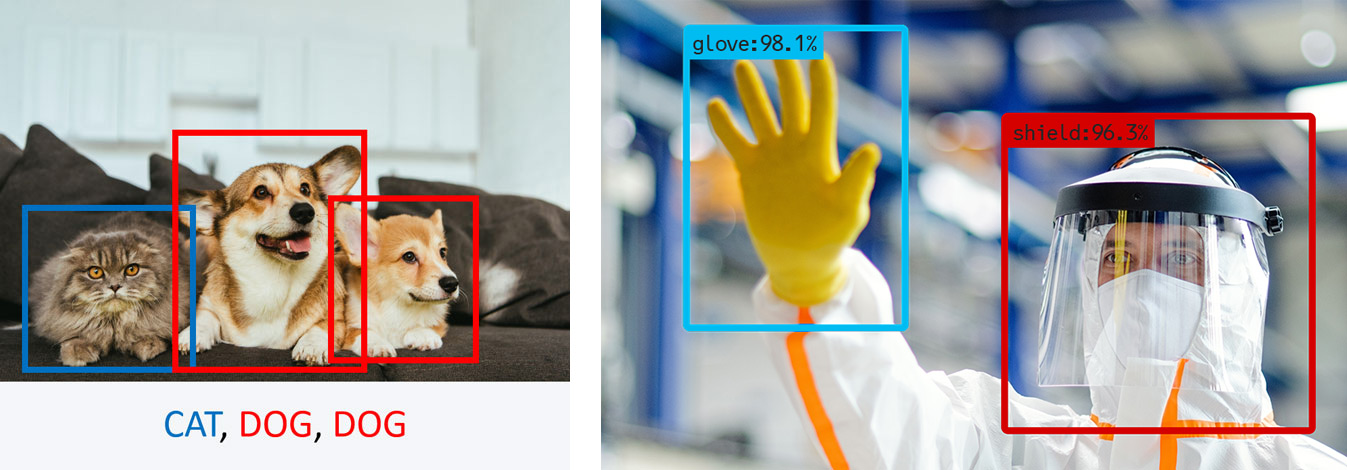

Deep learning technology is not only able to learn from positive results, but from mistakes as well: if the results are incorrect, certain parameters are varied as part of the training process, whereupon the system restarts the process. The software repeats this procedure until the model is optimally trained for the respective application.
What Are Typical Applications of Machine Vision in the Manufacturing Industry?
Modern Machine Vision systems use AI methods and techniques such as machine learning or deep learning, and artificial neural networks. Supported by AI, the systems are able to perform complex tasks. Machine Vision recognizes objects, can determine properties, classify objects and make decisions based on this information.
Machine Vision represents a key technology for the automation of Industry 4.0 processes. The most important application areas of Machine Vision are the monitoring and control of industrial manufacturing processes to improve efficiency and safety. Machine Vision and Edge AI systems are typically used in quality control, assembly control, process control and robotics.
These systems perform complex tasks in a wide variety of manufacturing industries, such as the automotive industry, food industry or the pharmaceutical industry.
Typical applications of Machine Vision in factories are:
Quality Control and Assurance
- Inspection of complex surfaces (e.g. weld seams, semiconductors, leathers, web materials such as wire)
- Detection of production errors, deformations or anomalies (e.g. subtle scratches, dings, dents, particles, corrosion, foreign objects)
- Detection of machine defects (e.g. bolts becoming loose)
- Machine health supervision and failure prediction (so-called “predictive maintenance”)
- Inspection of geometric shapes and dimensions (e.g. wheel inspection in the automotive industry)
- Inspection of internal structures (by X-ray, heat flow thermography, or – in the near future – even magnetic resonance imaging known from medical diagnostics)
Operational Control and Process Efficiency
- Position recognition of objects (e.g. for robotic operations, conveyor belts, 3D-vision-assisted product assembly)
- Object recognition and automated classification (e.g. for tracking and tracing individual components)
- Object counting (e.g. for automated warehousing, inventory management, completeness checks of packaging and contents)
- Optical character recognition – OCR (e.g. capturing of text, symbols, number plates)
- Label edge recognition (e.g. for high-precision die cutting)
- Non-contact object measurement in 1D, 2D or 3D (e.g. for dimensional accuracy control or volume checks)
- Monitoring of factory worker movements (e.g. for efficiency control, motion analysis)
- Automated sorting of bulk cargo (e.g. foodstuff, granulates, stones and debris of all kinds)
Safety and Security on the Shop Floor (also see our dedicated blog article)
- Detection of safety gear (e.g. proper wearing of helmets, safety vests)
- Monitoring of safe zones and compliance with safety distances (e.g. distance of a factory worker from moving machinery)
- Detection of hands and foreign objects (e.g. in close proximity to machines)
- 3D person measurement and posture detection (e.g. for accident prevention and detection)
- Detection of security violations (e.g. unauthorized access, suspicious movements)
Common Challenges – And Why Manufacturers Must Consider the Data Workflow From End to End
In the smart “Factory of the Future”, Machine Vision and AI technology will be crucial components for process automation and the increase of efficiency. As products become more complex, innovative technologies are required to meet the increasing demands of quality management. Given the exorbitant amounts of Big Data generated by IoT devices and sensors, companies naturally face an unprecedented challenge, trapping many businesses in the pilot stage. Why is that?
1. The individual expectations on data analytics vary as its potential is vast and new technologies are emerging constantly. As there are many potential use cases for utilizing Machine Vision and AI in manufacturing, a lot of companies fail when trying to tackle too many objectives at once. Not only is it important to get an in-depth understanding of which technology is best suited for solving specific business problems, but to define goals that can be measured precisely.
Companies sometimes get stuck in the pilot stage when project milestones are not explicitly defined, when improper tools are chosen, and when there is no strategic guideline on whether or not results are to be considered a success. Considering ourselves “digital transformation partners”, Avinton is proud to have gained cross-industry experience in strategically collaborating with our global clients.
2. As diverse as the strategic objectives, is the data that is generated by various machines and other sources on the shop floor. A lot of it has been aggregated over decades, having lied idle in a completely unstructured state. Usually, less than 30% of data found at large corporations is ready to use, presenting a serious challenge for data practitioners.
In order for manufacturers to routinely work with Big Data, this issue has to be addressed right from the beginning. There needs to be infrastructure implemented that is capable of mapping data to assets at a global scale, spanning multiple machines, sensors, lines, and factories. Infrastructure that fully automates the data workflow from collection to analysis.
Bringing together the latest technologies from around the world and experience from working with international customers, our data architects have developed the Avinton Data Platform. Its purpose is to cover the entire data workflow from end to end. It is a solution flexible enough to meet the diverse requirements of our customers.
Avinton Data Platform provides the necessary infrastructure to collect, store, process and analyze Big Data using adaptable AI algorithms. It is a powerful, fast and yet cost-efficient data management solution that stays fully scalable for future needs. With Avinton Data Platform, it is our goal to deliver an elegant all-in-one solution for companies from various industries to generate business intelligence and value from their Big Data.
If you are considering the implementation of Machine Vision and AI technology into your company, please feel free to reach out to us. We will be happy to discuss how these new technologies can contribute to achieving your strategic goals – whether it be the assurance of product quality, improving process efficiency, or ensuring worker safety and security. We are looking forward to hearing from you!
We will be happy to provide you with more information.