Table of Contents
Digital transformation has become a critical part of business strategy for a company to survive. But what exactly does “digital transformation” mean and what are the roles of Big Data and AI?
In this article, we share our insights from guiding industry-leaders to become data-driven companies. Learn about the importance of data analysis and the challenges of implementing digital technology into all areas of business.
Key Take-Aways
- Digital transformation describes the radical rethinking of how organizations utilize digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Edge Computing, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- While established corporations are naturally risk-averse, speed and agility have become necessary features to stay competitive in markets increasingly disrupted by newcomers such as startups.
- Holistic digital transformation affects each and every part of a business. It will significantly impact business processes, the business model, the business domain, and company culture.
What Is Digital Transformation?
We are now living in the era of Big Data and AI, where data lies at the foundation of all important business decisions and strategies. As related technologies are emerging ever so fast, these times of constant change pose a threat to established corporations on the one hand while presenting them with unprecedented opportunities on the other. While the term “digital transformation” itself is not brand-new, its relevance for businesses from all industries has significantly increased in recent years. It describes the radical rethinking of how companies utilize digital tools, processes, and people to change business performance at its core. Companies have come to realize that the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business is not a choice. It has become a critical part of business strategy to stay competitive, differentiate products and services, and drive efficiency.
What are IoT, Edge Computing, Big Data, and AI?
Before we continue, let’s briefly discuss some of the most used – and usually interconnected – technologies in digital transformation. These are the Internet of Things (IoT), Edge Computing, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- The Internet of Things (IoT) consists of physical objects that have technology embedded (such as sensors or software). These devices are connected to a network or the cloud to transmit and exchange the data generated. IoT devices are not limited to an industry by any means. In fact, IoT is already widely applied in various fields – ranging from smart factories and smart agriculture to autonomous driving in the automotive industry and smart home automation for end users.
- Edge computing is related to IoT, as it solves the typical cloud-related challenges of network congestion and latency. “Edge” indicates that complex tasks aren’t performed on a remote cloud, but on the “edge of the network”. With edge computing, AI-powered data analysis or image classification takes place on the actual smart device (such as an Edge AI Camera) which allows for bandwidth reduction and real-time inferences. Especially in situations in which every millisecond counts – such as the safety of autonomous vehicles or worker’s safety on shop floors – speed is of the essence.
- Big Data describes the systematic approach of turning data into actual business value. While the amount of data available to companies is dramatically increasing, so is the number of different sources and formats. In order to derive business intelligence from such data, it first has to be collected, accumulated, processed, and analyzed.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a wide-ranging field in computer science. It describes intelligence demonstrated by smart machines to perform tasks that previously required human intelligence, such as learning and problem-solving. In the field of data science, AI-driven data analysis unlocks unprecedented insights. Machine learning algorithms not only detect patterns but reveal highly accurate forecasts and opportunities for optimization.
Corporations Are Naturally Risk-Averse
Naturally, radical changes are always associated with a high risk. Large corporations, therefore, tend to hesitate when it comes to implementing new technologies into their core business. This might explain why many corporations still view the term “digital transformation” too narrowly.
In this article, we want to explain why digital transformation is not to be understood as a “to-do list” on which single items can be checked as “done”. It’s not “just a countermeasure” against the potential for disruption from startups. Digital transformation is an ongoing process that requires full strategic commitment – ideally led by the CEO in close cooperation with the CIO and other senior managers – and profound operational knowledge in order to be successful and sustainable.
What Is the Difference Between Digital Transformation and Corporate Innovation?
Before taking a closer look at the challenges and opportunities associated with the incorporation of new technology, it’s important to differentiate the terms “digital transformation” and “corporate innovation”. Unfortunately, these terms are frequently misused or used interchangeably, which leads to confusion.
Let’s think about a freight ship, for a moment. Having the technological framework alone is not enough to make it leave the harbor and create value. A freight ship needs a crew that not only sets the route, but that is capable of navigating it safely to its destination. Accordingly, corporate innovation can be understood as the necessary force to set strategic goals, giving creative impulses and steering the actual process.
Transformation, however, can best be described as the journey itself. It is the journey from a status quo to an improved state of things. Like in our freight ship example, the success of the business relies on the availability of modern tools to solve specific problems, efficient processes, and a capable crew that shares a similar mindset.
It becomes clear that it’s not about one domain versus the other. Actually, digital transformation and corporate innovation are inextricably linked with each other.
Speed and Agility Are Key To Survive
In challenging times, innovation becomes a key factor for corporations to survive and to stay competitive. Startups, for example, are able to develop new technologies faster and they are more agile to adapt to change thanks to their small size. As a result, many established corporations feel threatened. They have, after all, a running business to primarily focus on and invest its resources in. It is necessary to make immediate profits in order to satisfy existing customers and shareholders.
We have experienced how society and the economy can change from one moment to another, not least because of the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. Existing business models might not be future-proof and sustainable after all. When the whole world is changing, it’s crucial to adapt in order to survive. That’s why established corporations need to ask themselves not only how they handle this challenge, but also how quickly – because when it comes to innovation, speed and agility are crucial.
Established companies do have some major advantages over small startups, after all: they have an existing large customer base, broad technological and industry know-how, human resources, and financial assets. But in the era of digital transformation, there’s another tremendously valuable asset: data. And established companies can access massive amounts of such.
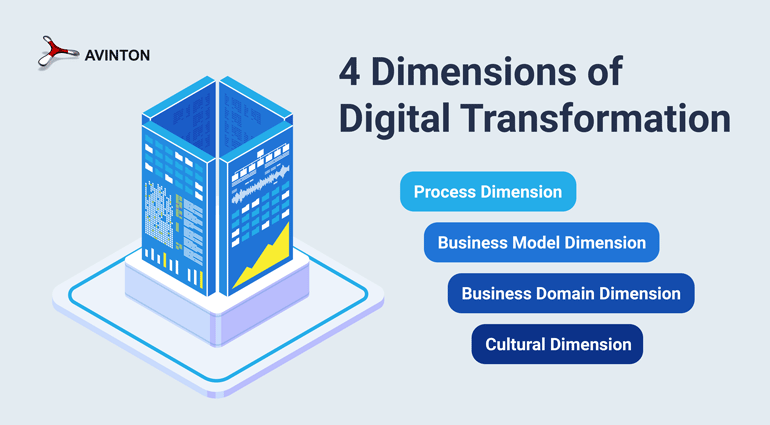
4 Dimensions of Digital Transformation
By now it should be clear that digital transformation is not one-dimensional. In fact, disregarding the multiple levels of its anatomy is one of the main reasons why transformation endeavors fail. It is a comprehensive approach affecting all areas of a business. Andrew Annacone, Managing Director of TechNexus, notes that many companies focus solely on the process or organizational transformation, while there are actually four levels on which fundamental change is necessary to “future-proof” a company.
1. Process Dimension
We have mentioned the relevance of data already. Today, there is more data being generated than ever before. But all this data is worthless – if it’s just lying idle, that is. Future technologies rely on how companies perform data analysis and make use of such “Big Data”.
What was once the revolutionary invention of the world’s first moving assembly line by Henry Ford, is now with AI. It profoundly changes the way companies work. On an operational level, AI technologies like machine learning can improve the efficiency of processes and significantly reduce the costs of production.
Technologies like edge computing allow AI devices to perform complex tasks right on the spot, even when there is no network connection. This is a major advantage over conventional cloud-based approaches. AI models can be trained in various ways, based on a company’s specific requirements and strategic goals.
The manufacturing industry, for example, utilizes so-called Edge AI cameras on the shop floor to detect defects in materials through AI image analysis. That way, material failures in the final products can be avoided. AI models can also be trained to detect foreign objects (such as metal parts or hands) in machinery, not only preventing costly mechanical breakdowns but also dangerous accidents on the shop floor.
Transforming organizational processes through digital technologies paves the way for so-called “smart factories” and “smart agriculture”.
2. Business Model Dimension
More and more companies are utilizing digital technologies to transform traditional business models. After all, not only technology is constantly changing – so is the market. The way a company generates value at the moment might be obsolete in the near future.
Instead of basing strategic decisions on assumptions and estimations, the collection of Big Data now enables companies to tap real-life and real-time usage information. After accumulating and processing this data, data analysis powered by AI algorithms detects unique patterns – such as shopper behavior and moods in the retail industry, or vehicle usage and maintenance frequency in the automotive industry.
Unprecedented opportunities for innovation can range from improving existing or launching new products, expanding to untapped markets and promising new distribution channels, or rethinking how revenue is generated.
As well-known examples for business model transformation, Andrew Annacone lists Netflix’s reinvention of video distribution and Apple’s reinvention of music delivery through iTunes. Product innovation, which is closely linked to this topic, means developing, re-designing, or substantially improving the actual product. It is not just about introducing something new and shiny to the market but adding a real benefit for the customers.
Adding AI to everyday devices, for example, can make people’s lives safer (smart surveillance, smartwatches, intelligent car sensors) or more convenient (smart assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri, or the automation of repetitive and redundant tasks). The Japanese insurance company JustInCase, for example, aims to make insurance services more accessible. They allow for insurance contracts to be concluded right on their smartphone app. The app also connects to the smartphone’s built-in sensors. If AI detects an active lifestyle, users are rewarded with discounts on their health insurance premiums.
3. Business Domain Dimension
Going one step further, domain transformation describes how established companies from a specific industry enter another domain. What was once considered an insuperable technological gap, has now narrowed and, in some cases, even become a logical step – all thanks to the large availability of digital technologies.
Naturally, domain transformation might sound like an unnecessarily risky endeavor. It seems only logical to further invest in a company’s proven core strengths to expand the current market share. But if industry boundaries keep blurring and former “non-competitors” disrupting the industry, at some point, it might become a must in order to survive. An organization is well-advised to stay proactive and consider unlocking the potentials lying within new business.
Amazon, for example, started out as an online retailer. At some point, it decided to also provide on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs on a pay-as-you-go basis. This subsidiary, Amazon Web Services, has become a major player that has forever changed the IT industry.
Implementing new technologies, such as machine learning in data analysis, as part of a holistic digital transformation process, will be the starting point of uncovering new business opportunities – even in previously untapped business domains.
4. Cultural Dimension
Digital transformation is a long-term change process affecting all areas of a business. It can only be as successful as this change is backed and implemented by both the management and the employees. In order for new technologies to manifest and for corporate innovation to thrive, it’s an essential first step to achieve a common mindset.
Traditionally, most companies have zero tolerance for failure, as failure typically translates to the loss of valuable resources or revenue. Working with digital technologies, such as Big Data and AI as a driver for corporate innovation, requires a certain level of experimenting, failing, and iterating. The “lean startup” approach follows the principle of “fail fast, learn faster”. That means, if you fail fast (in an isolated testing environment, that is), you gain valuable insights while not losing a massive amount of money.
Like with all change processes related to human beings, communication plays a central role in creating a shared mindset. Digital transformation, therefore, encompasses more than just acquiring new skills to use digital technologies. It includes learning how to adapt to the ever-changing digital world and getting comfortable with failing in innovation environments.
Furthermore, digital transformation also calls for redesigned recruiting processes, as the competition for tech-savvy talents – such as data engineers, data scientists, or innovation managers – increases globally.
Avinton Is Empowering Organizations
Avinton has been handling data-orientated projects in various domains long before terms like Big Data and AI gained the degree of recognition that is seen today. Today, most of the ongoing projects are focusing on Big Data and AI solutions. By providing innovative data management and data analysis software, we equip our customers with all the tools required for successful digital transformation endeavors.
We offer a range of services to suit your specific needs, from in-house solutions targeted at data management and AI with machine vision, to high-level IT consulting services and sourcing of on-site engineering talent.
Keep on reading. In this next article, we will focus on the six steps to become a data-driven company and discuss why many digital transformation initiatives fail.
We will be happy to provide you with more information.


